Exposure DB schema
The exposure schema was developed based on GEM Taxonomy 2.0 to accommodate the most important spatial features commonly employed in risk analysis to identify and estimate exposed value. The GED4ALL database schema contains the following tables: contribution, exposure_model, asset, occupancy, cost, cost_type, and tags.
Multiple types of structural/infrastructure assets and socio-economic exposure can be stored in the exposure database with attributes relevant to assessing risk from multiple hazards. The exposure schema provides 11 defined exposure types, for consistent classification of assets in different datasets: Residential, Commercial, Industrial, Healthcare, Education, Government, Infrastructure, Crop, Livestock, Forestry, and Mixed (as in cf_common.occupancy_enum). The tables include general attributes that can be adapted to each asset type. More specific indicators can be stored using the tags table, e.g. population gender and age, urban growth rate, GDP or others.
Exposure can be stored at multiple scales and using polygon (e.g., for a building footprint or number of buildings in a district), polyline (e.g. road network segment), and point (e.g. geolocated building at a lat,lon position). Exposure units can be assigned the number night-time or day-time occupants, to represent population exposure.
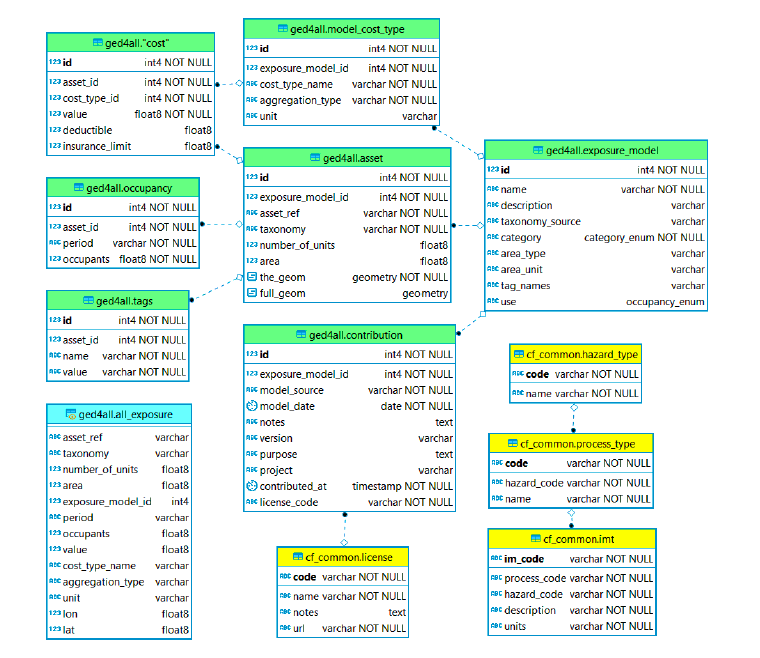 ERD (exposure schema): exposure table contents (green) and links to common tables (yellow). The schema includes a SQL view (cyan).
ERD (exposure schema): exposure table contents (green) and links to common tables (yellow). The schema includes a SQL view (cyan).
Table: ged4all.exposure_model
Each row in this table represents a collection of assets with a taxonomy_source (GEM Taxonomy, SynerG, FAO, etc) and category (buildings, road network, etc). A model can optionally contain one or more cost types (see model_cost_type), e.g. structural, contents and can also optionally contain information about the area occupied by the assets. Finally, a model can optionally specify any number of "tags", which can be applied to each asset.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | name | VARCHAR | Name of exposure model | |
| description | VARCHAR | Description of exposure model | ||
| taxonomy_source | VARCHAR | Name of taxonomy source | ||
| * | category | ENUM | ged4all.category_enum | Type of asset |
| area_type | VARCHAR | Aggregated or per asset | ||
| area_unit | VARCHAR | Unit of measure of area | ||
| tag_names | VARCHAR | Additional tag information | ||
| use | ENUM | cf_common.occupancy_enum | Usage type of the asset (e.g. residential, commercial) |
Table: ged4all.asset
Each row in the asset table represents a single asset or collection of assets, such as a building, aggregated collection of buildings, an item in an infrastructure network, or an area of farmland. The number_of_units field is used to specify the number of assets of this type at this location. The taxonomy value must be set to a valid taxonomy string using the taxonomy system specified in the exposure_model table, and identifies the typology of this asset.
There are two geometry fields providing geospatial information: - The "the_geom" field specifies a single point location and can be considered as a composite representation of latitude, longitude and a reference to WGS84. Only Point geometries are stored in this field. - The "full_geom" field is an optional representation of any geometry type (point, line, polygon, multipoint, multi-line, etc.) supported by the standard and can be used to describe the footprint of a building, regional boundaries, or lifelines.type (point, line, polygon, multipoint, multi-line, etc.) supported by the standard and can be used to describe the footprint of a building, regional boundaries, or lifelines.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | exposure_model_id | INT | ged4all.exposure_model | Unique number ID of source exposure model |
| * | asset_ref | VARCHAR | Alphanumeric code supplied by user | |
| * | taxonomy | VARCHAR | Alphanumeric code for the taxonomy source | |
| number_of_units | FLOAT | Number of assets represented | ||
| area | FLOAT | exposure_model.area_unit | Area of the asset in the units specified | |
| * | the_geom | GEOM | Associated geometry data (point location) | |
| full_geom | GEOM | Associated geometry data (polygon, multiline, multipolygon...) |
Table: ged4all.cost_type
Each exposure model can optionally have one or more types of cost associated with loss or damage to assets. For example, the cost of the building structure by square meter or the cost of the contents of a single building. Each cost type entry describes a category of cost, an aggregation type and a unit.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | exposure_model_id | INT | ged4all.exposure_model | Unique number ID of source exposure model |
| * | cost_type_name | VARCHAR | Type of asset cost (structural, non-structural, contents, business interruption) | |
| * | aggregation_type | VARCHAR | Aggregated or per asset | |
| unit | VARCHAR | Cost unit of measure |
Table: ged4all.cost
Each row in the cost table represents a cost of a given cost type for a given asset. The asset_id and cost_type_id fields are foreign keys used to identify an asset and model_cost_type. The value field provides the actual cost value in the unit specified in the corresponding model_cost_type entry.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | asset_id | INT | ged4all.asset | Unique number ID of the asset |
| * | cost_type_id | INT | ged4all.cost_type | Unique number ID of the cost type |
| * | value | FLOAT | Cost value | |
| deductible | FLOAT | |||
| insurance_limit | FLOAT |
Table: ged4all.occupants
The occupancy table is used to store information about the occupants of an asset in a given period, for example, the number of people in a given building during the day and during the night. For some cases the period might refer to a season, for example when considering livestock or agricultural assets. In some communities the term "occupancy" is used to refer to building usage, for example "industrial" or "residential"; this concept can be modelled in the GED4ALL schema using tags and/or by using a taxonomy system that supports building usage specification, such as the GEM Building Taxonomy.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | asset_id | INT | ged4all.asset | Unique number ID of the asset |
| * | period | VARCHAR | Occupancy type (night/day) | |
| * | num_occupants | FLOAT | Number of occupants |
Table: ged4all.tags
Each row in the tags table represents a name and value pair for a given asset. The asset_id is a foreign key used to identify an asset. The name field represents the name of the tag while the value field contains the associated value. Tags may be used to store any named scalar information with an asset, but in particular are useful for storing socio-economic indicators and their associated values, and also for grouping assets into census tracts, for example.
| Req | Field name | Type | Reference table | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| * | id | INT | Unique number ID | |
| * | asset_id | INT | ged4all.asset | Unique number ID of the asset |
| * | name | VARCHAR | Name of the tag | |
| * | value | VARCHAR | Number associated with the tag |
Types
| ENUM name | Types | Description |
|---|---|---|
| category_enum |
|
Type of asset category |
Taxonomy: GED4all
The exposure schema can accomodate different descriptions of assets using a taxonomy which describes their characteristics (e.g. building occupancy, construction, age, height, etc. or road surface type). The taxonomy being applied to a dataset is defined in ged4all.exposure_model.taxonomy_source. The taxonomy string, which describes all the characteristics of the asset (or group of assets of the same type), is defined at ged4all.asset.taxonomy.
We encourage the use of GED4all taxonomy, described in full here.
In order to summarise all the asset information into a single alphanumeric string, a tool will be provided, similar to the 'taxtweb' tool available from GEM dedicated to buildings taxonomy.
The taxonomy covers four main categories:
Buildings
The buildings taxonomy is based on GEM openquake taxonomy, with some semplifications. The taxonomy string is built as sequence of attributes separeted by slash:
MATERIAL/HEIGHT/DATE/OCCUPANCY/SHAPE/…
Missing attributes can be skipped from the string, e.g.
2-floors detached residential dwelling, reinforced concrete structure: CR/H:2/RES1
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Material of the Lateral Load-Resisting System (LLRS) | -- | Unknown material |
| C | Concrete, unknown reinforcement | |
| CU | Concrete, unreinforced * | |
| CR | Concrete, reinforced | |
| SRC | Concrete, composite with steel section | |
| S | Steel | |
| ME | Metal (except steel) | |
| M | Masonry, unknown reinforcement | |
| MUR | Masonry, unreinforced | |
| MCF | Masonry, confined | |
| MR | Masonry, reinforced | |
| E | Earth, unknown reinforcement | |
| EU | Earth, unreinforced | |
| ER | Earth, reinforced | |
| W | Wood | |
| MIX | Mixed materials (hybrid or composite) | |
| INF | Informal materials | |
| MATO | Other material | |
| Height | -- | Number of storeys unknown |
| H:n | n is the exact number of storeys above ground | |
| HBET:a-b | a-b is the range of number of storeys above ground (a=upper bound, and b= lower bound). a-b, range of number of storeys above | |
| HAPP:n | HAPP:n, approximate number of storeys above ground. | |
| Date of Construction or Retrofit | -- | Year unknown |
| Y :n | n is the exact date of construction or retrofit | |
| YBET:a-b | a nd b are the upper and lower bound for the date of construction or retrofit | |
| YPRE:n | n is the latest possible date of construction or retrofit | |
| YAPP:n | n is the approximate date of construction or retrofit | |
| Occupancy | -- | Unknown occupancy type |
| RES | Residential, unknown type | |
| RES1 | Residential, Single dwelling | |
| RES2 | Residential, Multi-unit | |
| RES2A | Residential, 2 Units (duplex) | |
| RES2B | Residential, 3-4 Units | |
| RES2C | Residential, 5-9 Units | |
| RES2D | Residential, 10-19 Units | |
| RES2E | Residential, 20-49 Units | |
| RES2F | Residential, 50+ Units | |
| RES3 | Residential, Temporary lodging | |
| RES4 | Residential, Institutional housing | |
| RES5 | Residential, Mobile home | |
| COM | Commercial and public, Unknown type | |
| COM1 | Commercial and public, Retail trade | |
| COM2 | Commercial and public, Wholesale trade and storage (warehouse) | |
| COM3 | Commercial and public, Offices, professional/technical services | |
| COM4 | Commercial and public, Hospital/medical clinic | |
| COM5 | Commercial and public, Entertainment | |
| COM6 | Commercial and public, Public building | |
| COM7 | Commercial and public, Covered parking garage | |
| COM8 | Commercial and public, Bus station | |
| COM9 | Commercial and public, Railway station | |
| COM10 | Commercial and public, Airport | |
| COM11 | Commercial and public, Recreation and leisure | |
| MIX | Mixed, unknown type | |
| MIX1 | Mixed use, Mostly residential and commercial | |
| MIX2 | Mixed use, Mostly commercial and residential | |
| MIX3 | Mixed use, Mostly commercial and industrial | |
| MIX4 | Mixed use, Mostly residential and industrial | |
| MIX5 | Mixed use, Mostly industrial and commercial | |
| MIX6 | Mixed use, Mostly industrial and residential | |
| IND | Industrial, unknown type | |
| IND1 | Industrial, Heavy industrial | |
| IND2 | Industrial, Light industrial | |
| AGR | Agriculture, unknown type | |
| AGR1 | Agriculture, Produce storage | |
| AGR2 | Agriculture, Animal shelter | |
| AGR3 | Agriculture, Agricultural processing | |
| ASS | Assembly, unknown type | |
| ASS1 | Assembly, Religious gathering | |
| ASS2 | Assembly, Arena | |
| ASS3 | Assembly, Cinema or concert hall | |
| ASS4 | Assembly, Other gatherings | |
| GOV | Government, unknown type | |
| GOV1 | Government, general services | |
| GOV2 | Government, emergency response | |
| EDU | Education, unknown type | |
| EDU1 | Education, Pre-school facility | |
| EDU2 | Education, School | |
| EDU3 | Education, College/university, offices and/or classrooms | |
| EDU4 | Education, College/university, research facilities and/or labs | |
| OCO | Other occupancy type | |
| Ground floor hydrodynamics | -- | Ground floor hydrodynamics unknown |
| GFO | Ground floor plan fully open (no walls) | |
| GFH | Ground floor plan partially open (i.e. with at least 50% of walls). | |
| GFM | Not open, many doors and/or windows (i.e. more than 20% of wall surface area). | |
| GFN | Not open, few doors and/or windows (i.e. less than 20% of wall surface area) | |
| Roof Shape | -- | Unknown roof shape |
| RSH1 | Flat | |
| RSH2 | Pitched with gable ends | |
| RSH3 | Pitched and hipped | |
| RSH4 | Pitched with dormers | |
| RSH5 | Monopitch | |
| RSH6 | Sawtooth | |
| RSH7 | Curved | |
| RSH8 | Complex regular | |
| RSH9 | Complex irregular | |
| RSHO | Roof shape, other | |
| Floor | -- | Floor material, unknown |
| FN | No elevated or suspended floor material (single-storey building) | |
| FM | Masonry | |
| FE | Earthen | |
| FC | Concrete | |
| FME | Metal | |
| FW | Wood | |
| FO | Floor material, other |
Lifelines
The lifelines taxonomy includes all infrastructures commonly found in populated areas, such as:
- Roads and railways
- Pipelines
- Energy generation and power grid
- Potable water and wastewater system
- Communication systems
Three main sources of information have been used for the definition of this taxonomy: FP7 EU Project Syner-G, HAZUS11 recommendations, and the OpenStreetMap (OSM) classification system.
Roads and railways
This taxonomy is strongly based on the classification system adopted by OpenStreetMap, since OSM is undoubtedly the largest and most complete source of open information concerning the location of roads and railways.
The taxonomy string is simply TYPE+CATEGORY, e.g.
Secondary road: RDN+SE
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Road network | RDN+MO | Motorway: restricted access major divided highway (i.e. freeway), normally with 2 or more running lanes plus emergency hard shoulder |
| RDN+TR | Trunk: the most important roads in a country's system that aren't motorways (not necessarily be a divided highway) | |
| RDN+PR | Primary: the next most important roads in a country's system (often link larger towns) | |
| RDN+SE | Secondary: the next most important roads in a country's system (often link towns) | |
| RDN+TE | Tertiary: the next most important roads in a country's system (often link smaller towns and villages) | |
| RDN+UN | Unclassified: the least important through roads in a country's system (often link villages and hamlets) | |
| RDN+RE | Residential: roads which serve as an access to housing, without function of connecting settlements. Often lined with housing. | |
| RDN+SR | Service: access roads to, or within an industrial estate, camp site, business park, car park etc. | |
| RDN | Unknown: no information concerning road typology | |
| Railway network | RLW+LR | Light rail: a higher-standard tram system, normally in its own right-of-way. Often reaches a considerable length (tens of kilometer) |
| RLW+MR | Monorail: a single-rail railway | |
| RLW+RL | Rail: full sized passenger or freight trains in the standard gauge for the country or state | |
| RLW+SW | Subway: a city passenger underground rail service running mostly grade separated | |
| RLW+TR | Tram: one or two carriage rail vehicles, usually sharing motor road. | |
| RLW | Unknown: no additional information concerning rail typology. |
Pipelines
The taxonomy presented herein has been developed using the classification experience developed in Syner-G and STREST (Crowley et al., 2016).
The taxonomy string is simply PPL/CONTENT/POSITION/MATERIAL/JOINT_TYPE/SOIL_TYPE/DIAMETER, e.g.
Large elevated pipe for potable water: CPW/PEL/DLG
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Content | CGS | Gas |
| COL | Oil | |
| CPW | Potable water | |
| CWW | Wastewater | |
| COT | Other content | |
| -- | Unknown | |
| Position | PBU | Buried |
| PEL | Elevated | |
| Material | MPC | Polyvinyl chloride |
| MPE | Polyethylene | |
| MCI | Cast iron | |
| MDI | Ductile iron | |
| MWS | Welded steel | |
| MRM | Reinforced plastic mortar | |
| MRM | Resin transfer moulding | |
| MAC | Asbestos-cement | |
| MC | Concrete | |
| MCL | Clay | |
| MO | Other material | |
| MUB | Unknown, brittle | |
| MUD | Unknown, ductile | |
| -- | Unknown material | |
| Joint type | JAW | Arc welded |
| JGW | Gas welded | |
| JCE | Cemented | |
| JFW | Fillet weld | |
| JBS | Bell and spigot (caulked) | |
| JRI | Riveted | |
| JMR | Mechanical restrained | |
| JSC | Screwed | |
| JRU | Rubber gasket | |
| JSG | Unknown, segmented | |
| JCO | Unknown, continuous | |
| JO | Other joint | |
| -- | Unknown joint | |
| Soil type | SCO | Corrosive |
| SNC | Non corrosive | |
| -- | Unknown soil type | |
| Diameter | DSM | Small (< 40 cm) |
| DLG | Large (≥ 40 cm) | |
| -- | Unknown diameter |
Energy generation and power grid
We follow the taxonomy adopted by HAZUS, which allows capturing the capacity (e.g. voltage) of the elements. For the purposes of assessing damage due to natural disasters, it is also relevant to identify the presence of anchorage and whether the elements have been designed according to a particular code. The taxonomy for component of the power grid can thus be presented in the following manner: PWG/ENERGYSOURCE/COMPONENT/ANCHORAGE/CODE PROVISIONS, e.g.
Electric ditribution line through pylones: PWG/SSM/ANC
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | OIL | Oil |
| GEO | Geothermal | |
| NUC | Nuclear | |
| HYD | Hydroelectric | |
| WND | Wind | |
| SOL | Solar | |
| TDL | Tidal wave | |
| GAS | Gas | |
| BIO | Biomass | |
| O | Other | |
| -- | Unknown | |
| Power Capacity | PC: | Value (integer) |
| -- | Unknown power capacity | |
| Power grid | SSL | Low Voltage (<115 KV) Substation |
| SSM | Medium Voltage (115-500 KV) Substation | |
| SSH | High Voltage (>500 KV) Substation | |
| DTC | Distribution circuit | |
| TMT | Transmission tower | |
| Grid anchorage | ANC | Anchored |
| AUN | Unanchored | |
| -- | Unknown anchorage | |
| Code provisions | CDN | No code (non-engineered) |
| CDL | Low code | |
| CDM | Moderate code | |
| CDH | High code | |
| C99 | Code provisions unknown |
Potable water and wastewater systems
Potable water systems are comprised by water treatment plants, storage tanks, pipelines and pumping stations, while wastewater systems are composed by wasterwater treatment plants, lifting stations and pipelines. Our classification is based on the HAZUS guidelines.
The alphanumeric taxonomy strings are:
PWR/COMPONENT/ANCHORAGE/CODE PROVISIONS for potable water
WWR/COMPONENT/ANCHORAGE/CODE PROVISIONS for wasterwater
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Potable water | PWR | |
| Component | PWS | Small potable water treatment plant (<50 MGD) |
| PWM | Medium potable water treatment plant (50-200 MGD) | |
| PWL | Large potable water treatment plant (>200 MGD) | |
| PPS | Small pumping plant (<10 MGD) | |
| PPM | Medium pumping plant (10-50 MGD) | |
| PPL | Large pumping plant (>50 MGD) | |
| Anchorage | ANC | Anchored |
| AUN | Unanchored | |
| -- | Unknown anchorage | |
| Code provisions | CDN | No code (non-engineered) |
| CDL | Low code | |
| CDM | Moderate code | |
| CDH | High code | |
| -- | Code provisions unknown | |
| Wastewater | WWR | |
| Component | WWS | Small wastewater treatment plant (<50 MGD) |
| WWM | Medium wastewater treatment plant (50-200 MGD) | |
| WWL | Large wastewater treatment plant (>200 MGD) | |
| LSS | Small lift station (<10 MGD) | |
| LSM | Medium lift station (10-50 MGD) | |
| LSL | Large lift station (>50 MGD) | |
| Anchorage | ANC | Anchored |
| AUN | Unanchored | |
| -- | Unknown anchorage | |
| Code provisions | CDN | No code (non-engineered) |
| CDL | Low code | |
| CDM | Moderate code | |
| CDH | High code | |
| -- | Code provisions unknown |
Communication systems
A communication system is comprised by offices dedicated to the reception and dissimination of information (e.g. telephones offices, call centers, TV stations, radio station, telecomunication stations), supporting transmitter towers and distribution circuits. The components have been classified based on the classification system proposed by HAZUS. For the purposes of assessing damage due to natural disasters, it is also relevant to identify the presence of anchorage and whether the elements have been designed according to a particular code.
The taxonomy string for the components of a communication system is:
COM/COMPONENT/ANCHORAGE/CODE
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Component | TRD | AM or FM radio transmitters |
| TTV | TV stations or transmitters | |
| TWE | Weather stations or transmitters | |
| TTT | Telecommunication transmitters | |
| TOT | Other stations or transmitters | |
| DTC | Distribution circuit | |
| Anchorage | ANC | Anchored |
| AUN | Unanchored | |
| -- | Unknown anchorage | |
| Code provisions | CDN | No code (non-engineered) |
| CDL | Low code | |
| CDM | Moderate code | |
| CDH | High code | |
| -- | Code provisions unknown |
Crops, Livestock and Forestry
The taxonomy for crops, livestock and forestry was defined based on existing classification systems supported by the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO). For crops, the classification system in the 2000 agricultural census programme was adopted. This system comprises a wide range of attributes such as growing cycle (temporary/permanent), crop species, crop variety, season, land type, amongst others. The taxonomy proposed herein uses the first and second categorization levels proposed by FAO, as well as the growing cycle (e.g. permanent or temporary). A simple alphanumeric code is attributed to each class of crop.
Crops
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Cereals | CRP1+1 | Wheat |
| CRP1+2 | Maize | |
| CRP1+3 | Rice | |
| CRP1+4 | Sorghum | |
| CRP1+5 | Barley | |
| CRP1+6 | Rye | |
| CRP1+7 | Oats | |
| CRP1+8 | Millets | |
| CRP1+9 | Other | |
| Vegetables and melons | CRP2+1 | Leafy or stem vegetables |
| CRP2+2 | Fruit-bearing vegetables | |
| CRP2+3 | Root, bulb, or tuberous vegetables | |
| CRP2+4 | Mushrooms and truffles | |
| CRP2+5 | Other | |
| Fruits and nuts | CRP3+1 | Tropical and subtropical fruits |
| CRP3+2 | Citrus fruits | |
| CRP3+3 | Grapes | |
| CRP3+5 | Berries | |
| CRP3+6 | Pome fruits and stone fruits | |
| CRP3+7 | Nuts | |
| CRP3+8 | Other | |
| Oilseed crops | CRP4+1 | Soya beans |
| CRP4+2 | Groundnuts | |
| CRP4+3 | Other | |
| Root/tuber crops with high starch or inulin content | CRP5+1 | Potatoes |
| CRP5+2 | Sweet potatoes | |
| CRP5+3 | Cassava Yams | |
| CRP5+4 | Other | |
| Beverage and spice crops | CRP6+1 | Beverage crops |
| CRP6+2 | Spice crops | |
| CRP6+3 | Other | |
| Leguminous crops | CRP7+1 | Beans |
| CRP7+2 | Broad beans | |
| CRP7+3 | Chick peas | |
| CRP7+4 | Cow peas | |
| CRP7+5 | Lentils | |
| CRP7+6 | Lupins | |
| CRP7+7 | Peas | |
| CRP7+8 | Pigeon peas | |
| CRP7+9 | Leguminous crops | |
| CRP7+10 | Other | |
| Sugar crops | CRP8+1 | Sugar beet |
| CRP8+2 | Sugar cane | |
| CRP8+3 | Sweet sorghum | |
| CRP8+4 | Other | |
| Other crops | CRP9+1 | Grasses and other fodder crops |
| CRP9+2 | Fibre crops | |
| CRP9+3 | Medicinal, aromatic, pesticidal, or similar crops | |
| CRP9+4 | Rubber | |
| CRP9+5 | Flower crops | |
| CRP9+6 | Tobacco | |
| CRP9+7 | Other | |
| Unknown crop | CRP |
Livestock
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Large ruminants | LVS1+1 | Cattle |
| LVS1+2 | Buffaloes | |
| LVS1+3 | Yaks | |
| Small ruminants | LVS2+1 | Sheep |
| LVS2+2 | Goats | |
| Pigs or swines | LVS3 | |
| Equines | LVS4+1 | Horses |
| LVS4+2 | Mules and hinnies | |
| LVS4+3 | Asses | |
| LVS4+4 | Other (e.g. zebras) | |
| Camels and camelids | LVS5+1 | Camels |
| LVS5+2 | Llamas and alpacas | |
| Poultry | LVS6+1 | Chickens |
| LVS6+2 | Ducks | |
| LVS6+3 | Geese | |
| LVS6+4 | Turkeys | |
| LVS6+5 | Guinea fowls | |
| LVS6+6 | Pigeons | |
| LVS6+7 | Other | |
| Other animals | LVS7+1 | Deer, elk, reindeer |
| LVS7+2 | Fur-bearing animals such as foxes and minks | |
| LVS7+3 | Dogs and cats | |
| LVS7+4 | Rabbits and hares | |
| LVS7+5 | Other (e.g. emus, ostriches, elephants) | |
| Insects | LVS8+1 | Bees |
| LVS8+2 | Silkworms | |
| LVS8+3 | Other worms or insects | |
| Unknown livestock |
Forestry
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Closed forest | FRT1+1 | Mainly evergreen forest - the canopy is never without green foliage, but individual trees may shed their leaves (e.g. Sumatra, Atrato Valley (Colombia), Atlantic slopes of Costa Rica, Amazon Basin). |
| FRT1+2 | Mainly deciduous forest - majority of trees shed their foliage simultaneously in connection to unfavourable season (e.g. North and South America, Southern slopes of the Himalayas and Europe) | |
| FRT1+3 | Extremely xeromorphic forest - dense stands of trees, composed by species such as bottle or tuft rees with succulent leaves (e.g. thorn forest in Southwestern North America and Southwestern Africa) | |
| Woodland | FRT2+1 | Mainly evergreen woodland - the canopy is never without green foliage, but individual trees may shed their leaves (e.g. Mediterranean Basin). |
| FRT2+2 | Mainly deciduous woodland - majority of trees shed their foliage simultaneously in connection to unfavourable season (e.g. Southern California and American Southeast, Mediterranean Basin) | |
| FRT2+3 | Extremely xeromorphic woodland - dense stands of trees, composed by species such as bottle or tuft rees with succulent leaves (e.g. Southwestern North America and Southwestern Africa) | |
| Scrub | FRT3+1 | Mainly evergreen scrub - the canopy is never without green foliage, but individual species may shed their leaves (e.g. Mediterranean dwarf palm shrubland, Chaparral shrubland in California or Hawaiian tree fern thicket). |
| FRT3+2 | Mainly deciduous scrub - majority of scrub shed their foliage simultaneously in connection to unfavourable season (e.g. peat mosses in Scotland) | |
| FRT3+3 | Extremely xeromorphic (subdesert) shrubland - very open stands of shrubs, often composed by vegetation with green branches without leaves, some of them with thorns (e.g. mulga scrub in Australia). | |
| Dwarf-scrub and related communities | FRT4+1 | Mainly evergreen dwarf-scrub - mostly dense dwarf scrub evergreen dominating the landscape (e.g. East Mediterranean mountains). |
| FRT4+2 | Mainly deciduous scrub - majority of vegetation shed their foliage simultaneously in connection to unfavourable season (e.g. Sierra Nevada in California ) | |
| FRT4+3 | Extremely xeromorphic dwarf-shrubland - more or less open formations consisting of dwarf-shrubs or succulent species (e.g. Australia). | |
| FRT4+4 | Tundra - slowly growing, low formations, consisting mainly of dwarf-shrubs beyond the subpolar tree line (e.g. Alaska, Northern Canada, Greenland, Norway, Finland and Siberia). | |
| FRT4+5 | Mossy bog formations with dwarf-shrub - peat accumulations formed mainly by mosses which generally cover the surface as well (e.g. Western Siberian Lowlands in Russia). | |
| Herbaceous vegetation | FRT5+1 | Tall graminoid vegetation - Mostly composed by tall grasslands with heights of over 2 m. Forbs can be presented but their coverage is less than 50% (e.g. Northeast Bolivia, African savannah and upper Nile Valley). |
| FRT5+2 | Medium tall grassland - Mostly composed by grasslands with heights between 0.5 and 2 m. Forbs can be presented but their coverage is less than 50% (e.g. Sahel region in Africa, Eastern Kansas, glasslands in New Zealand) | |
| FRT5+3 | Short grassland - Mostly composed by grasslands with heights below 0.5 m. Forbs can be presented but their coverage is less than 50% (e.g. alpine regions of Kenya, Colombia and Venezuela). | |
| FRT5+4 | Forb vegetation - the plant community if mostly composed by forbs (more than 50%). (e.g. Sonoran Desert) | |
| FRT5+5 | Hydromorphic fresh-water vegetation - mostly composed by aquatic plants that are structurally supported by water, in wet or flooded regions most of the year (e.g. Amazon Basin) |
Socio-Economic indicators
Natural hazards are a complex phenomenon featuring large number of interactions that result into loss of lives, livelihoods and interruption of systems. The socio-economic indicators are related to the capacity of populations to prepare, respond and recover from potential damage. For example, education theme is related to awareness, which is essential for a population to avoid and cope with a disaster. The Socio-economic Indicators taxonomy aims at identifying and describing a set of variables which provide a basis for understanding and measuring resilience, social vulnerability and economic vulnerability. The taxonomy system is divided into eight main themes (economy, education, environment, government and institutional capacity, index, health, infrastructure and population), each theme is later subdivided to different levels of detail. The eight main themes in the Socio-economic Indicator Taxonomy are the following:
- Population: defines community demographics: structure, distribution and size.
- Economy: measures the welfare and social security levels of communities
- Education: provides information about invested resources and expected outcome of education, access and participation to education
- Environment: defines the underlying conditions that make an environment susceptible to damage, disaster experience and prevalence
- Governance and institutional capacity: institutional performance and regulatory efficiency, corruption control and stability of political system
- Health: population health conditions and health sector capabilities
- Index: range of indexes that cover different sectors, for example, the Disaster Risk Index used by the United Nation Development programme to monitor the global evolution of risk.
- Infrastructure: Transportation and communication infrastructure, status and access to utility lifelines
Population
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Population Structure | POPPPSPOP | Population |
| POPPPSRPP | Rural population | |
| POPPPSRUB | Urbanization Rate | |
| POPPPSSRI | Sex ratio | |
| POPPPSUPR | Urban population | |
| POPPPSADP | Age dependency ratio | |
| POPPPSAPD | Average Population Density (areas over 400 ppl/km2) | |
| POPPPSCAO | Percentage of land area with over 400 people per km2 | |
| POPPPSIMP | Foreign Born Migrants | |
| POPPPSLPF | Labour force participation rate - Female | |
| POPPPSNMR | Net migration rate | |
| POPPPSPGR | Population growth rate | |
| Vulnerable Population | POPVNPSLP | Slum population in urban areas |
| POPVNPPUF | Population under 5 | |
| POPVNPPIP | Percentage of the population below income poverty line | |
| POPVNPITA | International tourism arrivals | |
| POPVNPFPP | Female Population | |
| POPVNPASE | Population over 65 | |
| POPVNPTPP | Refugees (country of origin) |
Economy
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Economic Activity | ECOEACVLE | Value lost due to electrical outages |
| ECOEACBEX | Budget expenditures | |
| ECOEACCDC | Carbon Dioxide Emissions | |
| ECOEACCPI | Consumer price index | |
| ECOEACEXS | Exports | |
| ECOEACFCE | Final consumption expenditure | |
| ECOEACFDP | Foreign direct investment, net inflows | |
| ECOEACGCE | General government final consumption expenditure | |
| ECOEACGFC | Gross fixed capital formation | |
| ECOEACGGE | Greenhouse gas emissions | |
| ECOEACGNC | GDP Nominal per population | |
| ECOEACGRB | General government revenue | |
| ECOEACGRN | GDP Nominal | |
| ECOEACGS1 | Gross savings | |
| ECOEACGUS | GNI per capita | |
| ECOEACHEE | Net Household final consumption expenditure | |
| ECOEACICR | Implied PPP conversion rate | |
| ECOEACIDA | Inflation, GDP deflator | |
| ECOEACIMP | Imports | |
| ECOEACIPD | Income payments (BoP) | |
| ECOEACMEP | Military expenditures | |
| ECOEAC039 | Adjusted savings: consumption of fixed capital | |
| ECOEACPCM | PPP conversion factor (GDP) to market exchange rate ratio | |
| ECOEACPEE | Remittance Inflows | |
| ECOEACPEP | Public expenditure on education | |
| ECOEACTIN | Total investment | |
| ECOEACTR1 | International tourism receipts as a percent of total exports | |
| ECOEACTRA | Trade | |
| ECOEACTRE | International tourism receipts as a percent of GDP | |
| Economic Resources | ECOERETRG | Total reserves (includes gold) |
| ECOERE040 | Adjusted savings: mineral depletion | |
| ECOERE042 | Adjusted savings: energy depletion | |
| ECOERE226 | Net ODA received per capita | |
| ECOEREBRE | Budget revenues | |
| ECOERECNT | Net taxes on products | |
| ECOEREDEX | Debt - external | |
| ECOEREGGD | General government gross debt | |
| ECOEREGNS | Gross national savings | |
| ECOEREGPC | GDP at purchasing power parity per capita | |
| ECOEREIRP | Inflation rate (consumer prices) | |
| ECOERELAP | Land use - arable land | |
| ECOERELCP | Land use - permanent crops | |
| ECOEREMQP | Money and quasi money (M2) | |
| ECOERENLB | General government net lending/borrowing | |
| ECOEREPDP | Public debt | |
| ECOERERDE | Research and development expenditure | |
| ECOERETRV | Tax revenue | |
| ECOERETTR | Total tax rate | |
| Economic Composition | ECOECPAGR | GDP composition by sector - agriculture |
| ECOECPWRT | Wholesale, retail trade, restaurants and hotels (ISIC G-H) | |
| ECOECPTSC | Transport, storage and communication (ISIC I) | |
| ECOECPSER | GDP - composition by sector - services | |
| ECOECPOTA | Other Activities (ISIC J-P) | |
| ECOECPMMU | Mining, Manufacturing, Utilities (ISIC C-E) | |
| ECOECPIND | GDP composition by sector - industry | |
| ECOECPCON | Construction (ISIC F) | |
| ECOECPAHF | Agriculture, hunting, forestry, fishing (ISIC A-B) | |
| Income Distribution and Poverty | ECOIDPLIS | Income share held by lowest 20% |
| ECOIDPPPL | Population below national poverty line | |
| ECOIDPPOG | Poverty gap at $2 a day (PPP) | |
| ECOIDPGIN | GINI index | |
| ECOIDPISF | Income share held by fourth 20 % | |
| ECOIDPISH | Income share held by highest 20% | |
| ECOIDPISS | Income share held by second 20 % | |
| ECOIDPIST | Income share held by third 20 % | |
| ECOIDPPGP | Poverty gap at $1.25 a day (PPP) | |
| Labour Market | ECOLAMLPT | Labor force participation rate |
| ECOLAMRRD | Researchers in R&D | |
| ECOLAMTEC | Technicians in R&D | |
| ECOLAMUEP | Unemployment Rate | |
| ECOLAMEAT | Employment in agriculture | |
| ECOLAMEIT | Employment in industry | |
| ECOLAMEPT | Ratio of youth employment to population ages 15-24 | |
| ECOLAMEST | Employment in services | |
| ECOLAMFLM | Female legislators, senior officials and managers | |
| ECOLAMLAF | Labor force | |
| ECOLAMLP1 | Female labor participation rate | |
| ECOLAMPET | Employment to population ratio ages 15+ | |
| Trade Economics | ECOTRECID | Cost to import |
| ECOTREMIC | Merchandise imports CIF | |
| ECOTREISS | Imports of goods and services | |
| ECOTRECED | Cost to export | |
| ECOTRE072 | Tariff rate, most favored nation, weighted mean, all products percentage | |
| ECOTREMTR | Merchandise trade | |
| ECOTREIGD | Imports of goods and services (BoP) | |
| ECOTREMEX | Merchandise exports to developing economies within region | |
| ECOTREEVI | Export volume index | |
| ECOTREEVE | Export value index | |
| ECOTREEEE | Merchandise exports FOB | |
| ECOTRECPT | Container port traffic (TEU: 20 foot equivalent units) |
Education
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Education Outcome | EDUEOCSAF | Female population without secondary education or higher |
| EDUEEOCCT | Primary School Completion Rate | |
| EDUEOCEYS | Expected Years of Schooling | |
| EDUEOCLFM | Ratio of young literate males to females ages 15-24 | |
| EDUEOCLFP | Illiteracy - female | |
| EDUEOCLMP | Illiteracy - male | |
| EDUEOCLTP | Illiteracy | |
| EDUEOCMYS | Mean Years of Schooling | |
| EDUEOCSAM | Male population without secondary education or higher | |
| EDUEOCSTJ | Scientific and technical journal articles | |
| Education Access | EDUEACEEG | Education expenditures |
| EDUEACPTS | Pupil-teacher ratio, secondary | |
| EDUEACPTP | Pupil-teacher ratio, primary | |
| EDUEACETG | Gross enrollment ratio, tertiary | |
| EDUEACSTG | Gross enrollment ratio, secondary | |
| EDUEACBGP | Ratio of girls to boys in primary and secondary education | |
| EDUEACEPG | Gross enrollment ratio, primary | |
| EDUEACCPT | Children out of school, primary |
Environment
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Disaster Prevalence | ENVDIPDFT | Droughts, floods, extreme temperatures |
| ENVDIPPLM | Population living in areas where elevation is below 5 meters | |
| ENVDIPINP | Natural disasters - Population affected | |
| ENVDIPIND | Natural disasters - Number of deaths | |
| ENVDIPDRR | Disaster risk reduction progress score | |
| Basic Geography | ENVGEOLAK | Land Area |
| ENVGEOCLK | Geographic Classification | |
| ENVGEOFAP | Forest area | |
| ENVGEOWAK | Water Area | |
| Landuse/Landcover | ENVLULALP | Arable land |
| ENVLULFEC | Fertilizer consumption | |
| ENVLULURP | Urban pollution | |
| ENVLULPCP | Permanent cropland | |
| ENVLULALA | Agricultural land | |
| Control of Corruption | GICPSCCOC | Control of Corruption |
| GICPSCCRI | Corruption Index | |
| Voice and Accountability | GICLRVSWP | Percentage of seats held by women in national parliaments |
| GICLRVVOA | Voice and Accountability | |
| GICLRVVTE | Voter Turnout at last parliamentary Election | |
| GICLRVOIR | Official information is available on request | |
| Rule of Law | GICLRVETD | Equal treatment and absence of discrimination |
| GICLRVSLR | Strength of legal rights index | |
| GICPSCROL | Rule of Law |
Governance
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Political Stability | GICAVTCCL | Civil conflict is effectively limited |
| GICPSCPSA | Political Stability and Absence of Violence | |
| GICAVTVRG | People do not resort to violence to redress personal grievances | |
| GICAVTLCP | Losses due to theft, robbery, vandalism, and arson | |
| GICAVTIHO | Intentional homicides | |
| Government Effectiveness | GICGEFGEF | Government Effectiveness |
| Regulatory Quality | GICGEFREQ | Regulatory Quality |
Health
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Health Status | HEAHSTFRT | Total fertility rate |
| HEAHSTLRM | Lifetime risk of maternal death | |
| HEAHSTMAL | Infectious and parasitic diseases: Malaria (DALYs) | |
| HEAHSTMEI | One-year-olds lacking immunization against - Measles | |
| HEAHSTTUC | Infectious and parasitic diseases: Tuberculosis (DALYs) | |
| HEAHSTMRI | Infant mortality rate | |
| HEAHSTMUF | Under 5 years mortality rate | |
| HEAHSTPUP | Prevalence of undernourishment | |
| HEAHSTUNC | Unmet need for contraception | |
| HEAHSTAAP | HIV/AIDS - adult prevalence rate | |
| HEAHSTBAS | Births attended by skilled health staff | |
| HEAHSTBRC | Crude birth rate | |
| HEAHSTDII | Infectious and parasitic diseases: Diarrheal diseases (DALYs) | |
| HEAHSTDPC | Dietary Protein Consumption | |
| HEAHSTDRC | Crude death rate | |
| HEAHSTLEX | Life expectancy at birth | |
| Healthcare Resources | HEAHCRHBE | Hospital beds |
| HEAHCREHP | Health expenditure, private | |
| HEAHCREPP | Health expenditure, public | |
| HEAHCRERH | External resources for health | |
| HEAHCRHAT | Health expenditure, total | |
| HEAHCRHEC | Health expenditure per capita | |
| HEAHCRNMW | Nurses and midwives | |
| HEAHCRPHY | Physicians |
Index
| Code | Description |
|---|---|
| INXHDIGIV | Inequality adjusted Human Development Index (Gender Inequality Index) |
| INXHDI012 | Human Development Index - 2012 |
| INXXXXSFI | State Fragility Index |
| INXXXXPOL | Polity Index IV |
| INXXXXLSC | Liner shipping connectivity index |
| INXXXXGEI | Gender Equity Index |
| INXXXXGBB | GEF benefits index for biodiversity |
| INXXXXEVI | Environmental Vulnerability Index |
| INXXXXESI | Environmental Sustainability Index |
| INXXXXDRI | Disaster Risk Index |
| INXLPICQL | Logistics performance index: Competence and quality of logistics services |
Infrastructure
| Attribute | Code | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Energy, Water and Sanitation | INFEWSNGC | Natural gas - consumption |
| INFEWSOCB | Oil - consumption | |
| INFEWSOPB | Oil - production | |
| INFEWSRFC | Renewable internal freshwater resources per capita | |
| INFEWSIWR | Rural population access to improved water source | |
| INFEWSACE | Population with access to electricity | |
| INFEWSECO | Electricity - consumption | |
| INFEWSEIP | Net energy imports | |
| INFEWSEPR | Electricity - production | |
| INFEWSEUP | Energy use (kg of oil equivalent) | |
| INFEWSISP | Population access to improved sanitation facilities | |
| INFEWSISR | Rural population access to improved sanitation facilities | |
| INFEWSISU | Urban population access to improved sanitation facilities | |
| INFEWSIWP | Population access to improved water source | |
| INFEWSIWU | Urban population access to improved water source | |
| Transport and Communication | INFTCOBRC | Fixed broadband Internet subscribers |
| INFTCOATF | Air transport, freight | |
| INFTCOTLC | Telephone lines | |
| INFTCORDE | Road density | |
| INFTCOQPI | Quality of port infrastructure, WEF | |
| INFTCOMVC | Motor vehicles | |
| INFTCOMCC | Mobile cellular subscriptions | |
| INFTCORWG | Railways, goods transported |